Gasoline Combustion: The Chemical Fire That Fuels Our World
Imagine a world without cars, planes, or many of the machines that power our modern lives. Hard to picture, right? At the heart of this mechanized world lies a fundamental chemical reaction: the combustion of gasoline. This seemingly simple process, the rapid oxidation of gasoline, is a chemical change that has shaped our world in profound ways. But is gasoline combustion a chemical change? Absolutely. Let's dive into the intricacies of this powerful transformation.
Gasoline, a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, undergoes a dramatic alteration when ignited in the presence of oxygen. This isn't simply gasoline disappearing; it's a fundamental rearrangement of its molecular structure. The chemical bonds within gasoline molecules break, and new bonds form with oxygen, creating different substances entirely – primarily carbon dioxide, water vapor, and heat. This change in molecular composition definitively answers the question: is the burning of gasoline a chemical change? Yes, and its implications are far-reaching.
The history of gasoline combustion is intertwined with the rise of the internal combustion engine. From the earliest experiments in the late 19th century, the potential of this chemical reaction to generate power became clear. The refinement of gasoline and the development of more efficient engines revolutionized transportation and industry, irrevocably changing the course of human civilization. The chemical transformation of gasoline into motion became the driving force behind a new era.
The importance of this chemical reaction cannot be overstated. It fuels our global transportation network, powers many of our industrial processes, and plays a vital role in generating electricity. However, the reliance on gasoline combustion comes with significant challenges. The environmental consequences, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, are a major concern. Understanding the chemical process underlying gasoline combustion is crucial for developing cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions.
The chemical equation for the complete combustion of octane, a major component of gasoline, provides a simplified view of the transformation: 2C8H18 + 25O2 → 16CO2 + 18H2O + Heat. This equation illustrates the fundamental rearrangement of atoms during combustion. The reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases significant energy in the form of heat, which is then harnessed to do work.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gasoline Combustion
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High energy density | Greenhouse gas emissions |
| Established infrastructure | Air pollution |
| Relatively inexpensive | Dependence on finite resources |
Several challenges arise from gasoline combustion. One major issue is incomplete combustion, which produces harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide. Another challenge is the efficient harnessing of the energy released during combustion. Solutions include catalytic converters to reduce emissions and ongoing research into more efficient engine designs. Additionally, the search for alternative fuels and energy sources represents a long-term solution to the challenges posed by gasoline combustion.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Is gasoline combustion a physical or chemical change? Chemical.
2. What are the byproducts of gasoline combustion? Primarily carbon dioxide, water vapor, and heat.
3. Why is gasoline combustion important? It powers transportation and industry.
4. What are the environmental impacts of gasoline combustion? Greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
5. What is the chemical equation for gasoline combustion? It varies depending on the specific hydrocarbons in the gasoline, but involves the reaction with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and heat.
6. What are some alternatives to gasoline combustion? Electric vehicles, hydrogen fuel cells, biofuels.
7. How can we reduce the negative impact of gasoline combustion? Improve engine efficiency, use catalytic converters, develop alternative fuels.
8. Is the burning of gasoline a chemical transformation? Yes.
In conclusion, gasoline combustion is a fundamental chemical change that has profoundly shaped our modern world. While its benefits are undeniable, so too are its environmental consequences. Understanding the intricate chemical dance of gasoline oxidation is crucial for mitigating these negative impacts and paving the way for a cleaner, more sustainable future. We must continue to explore alternative energy solutions while also improving the efficiency and cleanliness of gasoline combustion technologies. The future of our planet depends on our ability to harness the power of chemistry responsibly and innovatively.

Looking Good Co2 State Symbol Aerobic Equation For Respiration | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Write The Balanced Chemical Equation For Combustion Of Sugar C12h22o11 | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Chemical and physical properties of ethanol and gasoline | YonathAn-Avis Hai

What Is a Combustion Reaction | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Combustion Reaction Gasoline at Doris Vanburen blog | YonathAn-Avis Hai

is gasoline combustion a chemical change | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Chemical change in Combustion Science Fair Project | YonathAn-Avis Hai
+combusts.+2C8H18+%2B+25O2+16CO2+%2B+18H2O+%2BEnergy.jpg)
Gasoline Burning Chemical Equation at Beatrice Shaffer blog | YonathAn-Avis Hai

How To Write Combustion Reaction | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Car Engine Gasoline Chemical Change at Teressa Phillips blog | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Causes Of Misfire In Engines | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Balanced Chemical Equation For Combustion Of Gasoline | YonathAn-Avis Hai

is gasoline combustion a chemical change | YonathAn-Avis Hai
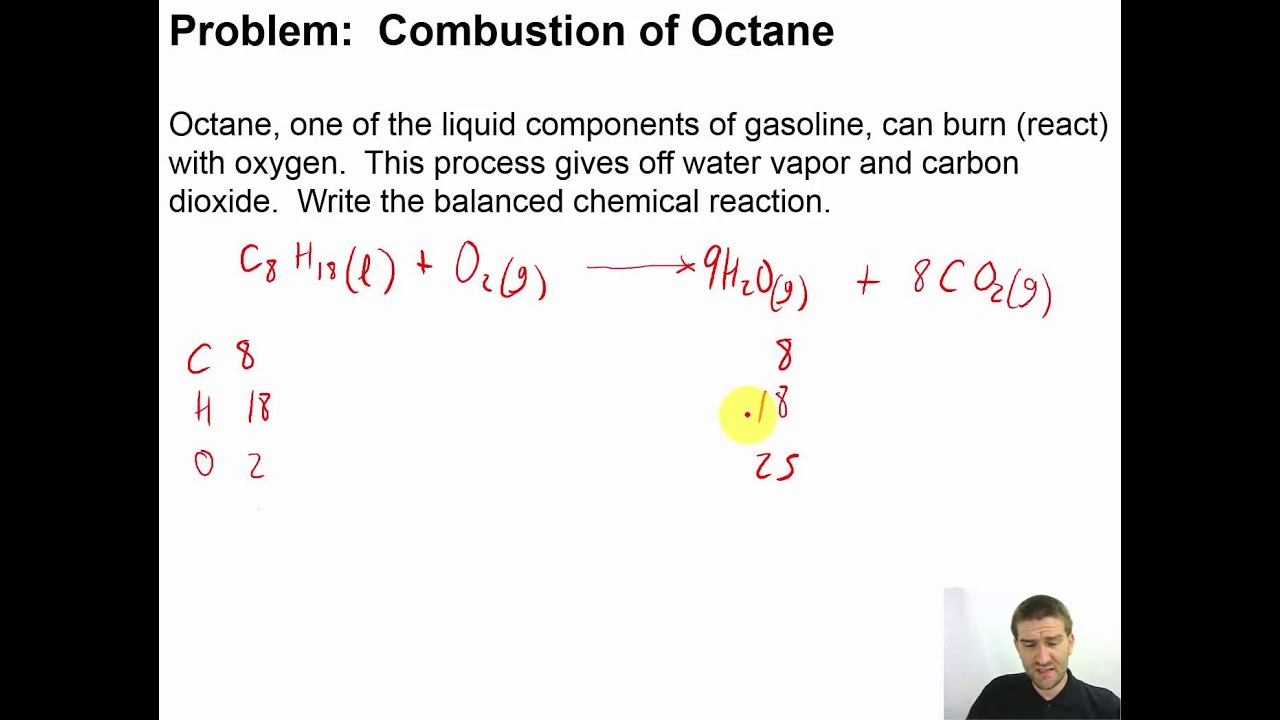
Balanced Equation For The Reaction Of Octane With Oxygen To Produce | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Balanced Chemical Equation For Combustion Of Gasoline | YonathAn-Avis Hai