Navigating the Malaysian Public Sector: A Look at Grade 48 Salary and Allowances
Embarking on a career in public service is a significant decision, often driven by the desire for stability and a defined career path. In Malaysia, the public sector operates on a structured salary scheme, with "gaji gred 48 termasuk elaun" representing a specific pay grade and its associated benefits, a point of interest for many aspiring and current civil servants. This article aims to demystify the intricacies of this salary structure, providing a comprehensive understanding of its implications and what it means for those within its scope.
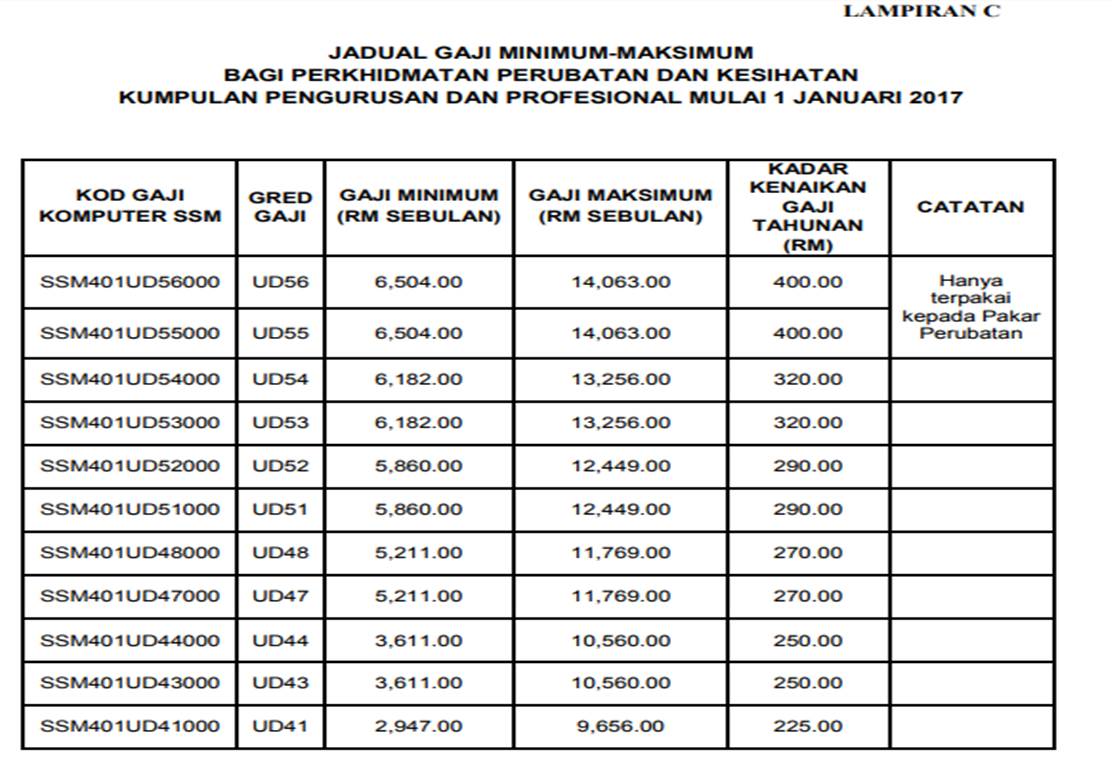
Imagine stepping into a system where your career trajectory is clearly laid out, with incremental advancements and corresponding salary increases. This is the reality for many within the Malaysian public sector. The concept of "gaji gred," literally translating to "salary grade," forms the backbone of this system. Each grade, from the entry-level to the highest ranking positions, comes with a predetermined salary range and a set of allowances, ensuring fairness and transparency in compensation.
The significance of "elaun," meaning allowances, cannot be overstated. These are additional payments on top of the base salary, designed to cover specific expenses or recognize the unique demands of certain roles. For instance, those in Grade 48 might be eligible for housing, transportation, and cost-of-living allowances, significantly augmenting their overall compensation package. Understanding these allowances is crucial for individuals to accurately assess their financial standing and make informed decisions.
However, the conversation around "gaji gred 48 termasuk elaun" isn't without its nuances. One common point of discussion revolves around its competitiveness compared to the private sector. While the public sector offers stability and a comprehensive benefits package, the private sector often boasts higher earning potential, particularly for in-demand skills and expertise. This dynamic creates a constant debate about attracting and retaining top talent within the public service.
Navigating the complexities of "gaji gred 48 termasuk elaun" requires a multifaceted understanding of its components, benefits, and potential drawbacks. By shedding light on these aspects, we aim to empower individuals with the knowledge to make informed career choices and optimize their financial well-being within the Malaysian public sector. Whether you're considering a career change, seeking promotion, or simply curious about this system, this guide serves as a valuable resource for navigating the intricacies of public sector compensation in Malaysia.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gaji Gred 48
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Job Security | Slower Salary Growth Compared to Private Sector |
| Comprehensive Benefits Package (Pension, Healthcare) | Limited Earning Potential Based on Fixed Salary Structure |
| Structured Career Progression Path | Bureaucracy and Potential for Slow Decision-Making Processes |

gaji gred 48 termasuk elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai

gaji gred 48 termasuk elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai

gaji gred 48 termasuk elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai
gaji gred 48 termasuk elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai

gaji gred 48 termasuk elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai

gaji gred 48 termasuk elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai

gaji gred 48 termasuk elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai

gaji gred 48 termasuk elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai

gaji gred 48 termasuk elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai