Stair Handrail Code: Building Safe and Compliant Staircases
Navigating the world of construction can feel like scaling a mountain, especially when it comes to regulations. But when it comes to stair handrail codes, compliance isn’t just a box to check—it’s the foundation of safe and accessible homes and buildings. Understanding these regulations ensures sturdy, reliable handrails that prevent falls and provide critical support for everyone.
Stair handrail regulations, essentially a set of guidelines dictating the design, installation, and dimensions of handrails, are paramount for ensuring stairway safety. These standards, often incorporated into building codes, provide a framework for constructors and homeowners to follow, ensuring consistency and minimizing risks associated with improper handrail construction. Ignoring these regulations can lead to dangerous staircases, potentially resulting in accidents and legal liabilities.
Historically, the need for standardized stair handrail construction emerged as buildings became taller and stairways more complex. Early building codes, while less comprehensive than modern versions, recognized the inherent dangers of unprotected stairways. Over time, as understanding of ergonomics and accessibility improved, handrail regulations evolved, incorporating specific measurements for height, width, and materials to maximize safety and usability for all individuals.
The core issue that stair handrail building codes address is fall prevention. A properly installed handrail provides a secure grip and support, mitigating the risk of tumbling down stairs, especially for children, the elderly, and people with mobility limitations. These codes cover various aspects, including handrail height, extensions beyond the top and bottom steps, clearance from the wall, and the strength of the materials used. This comprehensive approach aims to create a consistently safe environment, regardless of the specific staircase design.
Handrail codes define specific requirements for different types of buildings. For instance, residential building codes for handrails may differ from commercial building code requirements. These variations account for the anticipated usage patterns and potential risks associated with each setting. While the underlying principle of safety remains constant, factors such as occupancy load and building type influence the specific criteria.
Three key benefits arise from adhering to stair handrail building codes. Firstly, enhanced safety is the most obvious advantage. Compliant handrails drastically reduce the risk of falls, minimizing injuries and promoting a secure environment for all users. Secondly, compliance with these regulations safeguards builders and homeowners from legal liabilities. Adhering to established standards protects against potential lawsuits arising from accidents caused by non-compliant handrails. Finally, adherence to building codes can add value to a property. Prospective buyers often see compliance as a sign of quality construction and a commitment to safety, increasing a building's desirability.
Creating an action plan for handrail compliance starts with researching local building codes. Consult your local authorities or online resources to obtain the specific requirements for your area. Next, carefully measure your stairway, noting the rise, run, and overall length. Use these measurements to determine the appropriate handrail height, extensions, and other relevant dimensions. Finally, choose handrail materials and designs that comply with the code while also complementing your aesthetic preferences.
A simple checklist can help ensure compliance: Verify handrail height, check for proper extensions beyond the top and bottom steps, measure the clearance between the handrail and the wall, confirm the strength and durability of the chosen materials, and ensure proper installation methods are used. These checks ensure that your handrails meet all necessary safety standards.
Before starting construction, consult your local building department for specific regulations and permit requirements. Consider accessibility standards for individuals with disabilities, including proper handrail heights and graspable designs. Always use high-quality materials that can withstand anticipated loads and environmental conditions. Maintain detailed documentation throughout the construction process to ensure adherence to building codes and provide a record for future inspections.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Strict Handrail Building Codes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased safety and reduced falls | Can increase construction costs |
| Legal protection and reduced liability | May limit design flexibility in some cases |
| Enhanced property value | Requires thorough research and understanding of local codes |
Five best practices: 1. Consult local building codes. 2. Use durable materials. 3. Ensure proper handrail height and extensions. 4. Securely attach handrails to the wall or supporting structure. 5. Conduct regular inspections and maintenance.
Real-world examples can be found in various building types. Residential homes, commercial buildings, and public spaces all showcase the practical application of stair handrail codes. These codes provide a unified framework, ensuring consistent safety and accessibility in diverse environments.
Challenges can arise when retrofitting older buildings to meet current codes, but solutions exist through adaptable handrail designs and specialized installation techniques.
FAQs: 1. Where can I find my local building codes? 2. What is the standard handrail height? 3. What materials are acceptable for handrails? 4. What are the requirements for handrail extensions? 5. How do I inspect and maintain handrails? 6. Do handrail codes apply to all types of stairs? 7. Are there exceptions to handrail requirements? 8. How do I handle unique staircase designs when applying handrail codes?
Tips: Double-check measurements before installation. Ensure all connections are secure and stable. Consider adding non-slip surfaces to handrails for enhanced grip. Prioritize materials that are resistant to weathering and wear.
In conclusion, navigating the intricacies of stair handrail building codes might seem daunting, but it's an investment in safety and accessibility that pays dividends. Understanding and implementing these regulations not only prevents accidents but also ensures a building's compliance, protecting both occupants and owners. From enhancing safety and reducing liabilities to adding value to a property, adherence to these codes is a cornerstone of responsible construction. By prioritizing compliance, we create spaces that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also fundamentally safe and accessible for everyone. Take the time to familiarize yourself with your local building codes, engage with qualified professionals, and contribute to building a safer and more accessible environment for all. It’s an investment in peace of mind that will benefit everyone who uses your stairs.

Florida Building Code Stair Requirements | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Building Code For Stair Rails | YonathAn-Avis Hai
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stair-handrail-and-guard-code-1822015-FINAL1-5c054b4dc9e77c0001600219.png)
Down Stairs Handrail Height By Building Codes | YonathAn-Avis Hai

figure1en3gif 500550 again stairs measurement | YonathAn-Avis Hai

What Is Building Code For Stair Railing at Heather Ridout blog | YonathAn-Avis Hai

What Is Code For Step Height In Nc | YonathAn-Avis Hai

IBC Handrail International Building Code handrail railing guard | YonathAn-Avis Hai

building code for stair handrails | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Steel Handrail Thickness at Wilma Steppe blog | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Stair Handrail Width Code at Andre Martin blog | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Building Regulations For Stair Handrails | YonathAn-Avis Hai
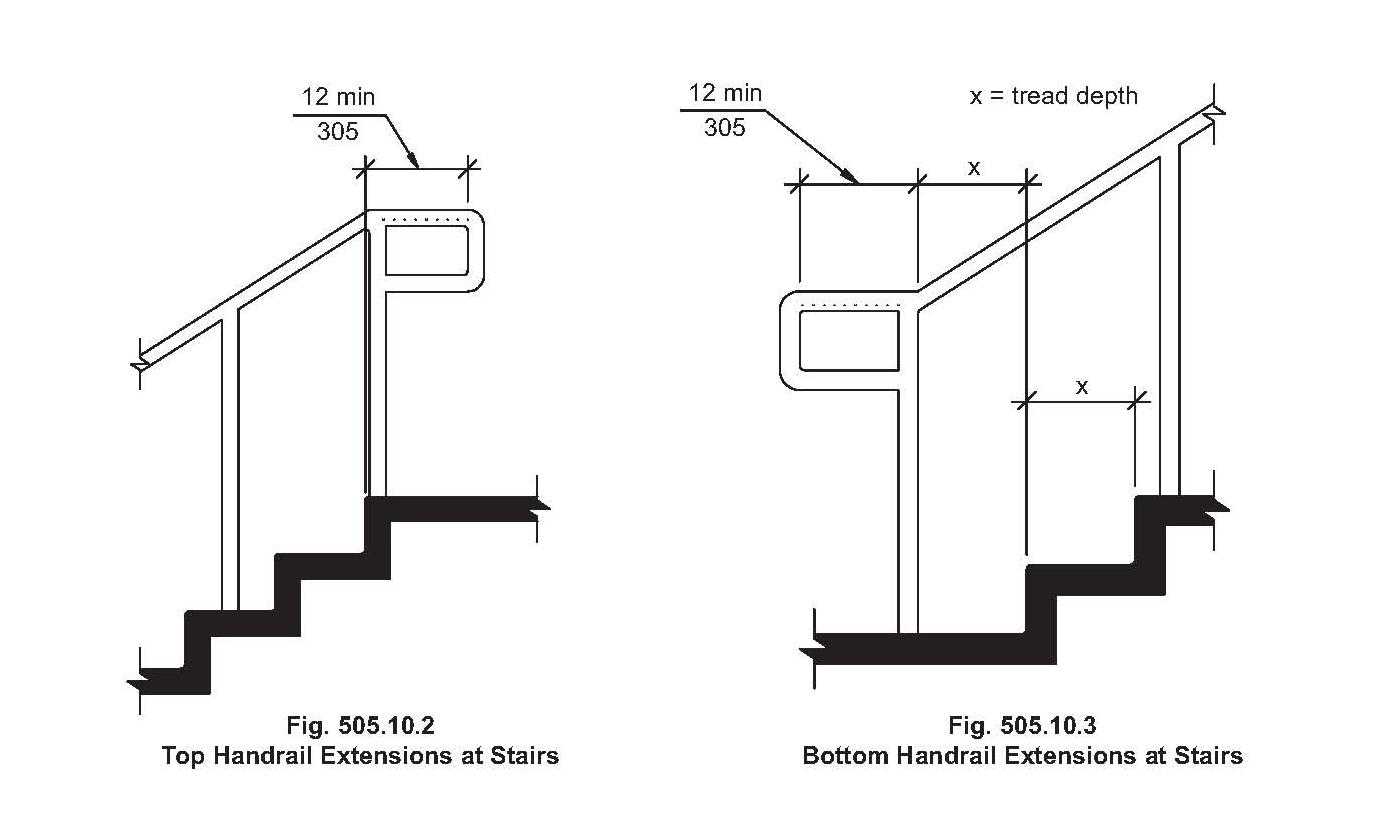
Ada Handrail Code Requirements at Krystal Hairston blog | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Grab Rail Building Code at John Horn blog | YonathAn-Avis Hai
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stair-handrail-and-guard-code-1822015-final-CJ-01-157768d7ac40439da36f9ba69faa00c6.png)
Stair Railing and Guard Building Code Guidelines 2023 | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Ontario Building Code For Stair Rails | YonathAn-Avis Hai