Understanding Malaysian Public Service Salary Grades and Allowances
Navigating the complexities of a country's public service employment system can be challenging, especially for those unfamiliar with the intricacies of salary structures and benefits. In Malaysia, the public sector remains a significant employer, attracting individuals seeking job security, a structured career path, and attractive benefits. Understanding the nuances of the salary and allowance system, often referred to as "gred gaji" and "elaun," is crucial for anyone considering a career in Malaysian public service.
This article aims to shed light on the key aspects of the Malaysian public service salary system, focusing on the principles that underpin the determination of salary grades and the various types of allowances provided. We will explore how these elements contribute to the overall compensation package, enabling prospective and current civil servants to make informed decisions about their careers.
The Malaysian public service salary system is meticulously designed to ensure fairness, transparency, and competitiveness. The system employs a graded structure where each grade corresponds to a specific salary range. This structure ensures that employees are compensated fairly based on their qualifications, experience, and responsibilities. Salary grades, often a point of interest for those exploring career options within the public sector, are pivotal in outlining potential earning potential and career progression.
A fundamental element of the Malaysian public service compensation package is the comprehensive range of allowances provided to employees. These allowances, separate from the base salary, are designed to cover various expenses and enhance the overall financial well-being of civil servants. Understanding the different types of allowances, eligibility criteria, and the calculations involved is essential for maximizing your potential earnings and benefits as a public servant.
This article will delve deeper into the specifics of salary grades and allowances, examining the historical context, their evolution over time, and the rationale behind their implementation. By the end of this article, readers will have a clearer understanding of the Malaysian public service compensation system and be better equipped to navigate its intricacies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Malaysian Public Service Salary System
Like any other system, the Malaysian public service salary structure has its own set of pros and cons. Understanding these can help potential and current civil servants make informed decisions:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Job security and stability | Slower salary progression compared to the private sector |
| Comprehensive benefits package including allowances, pensions, and healthcare | Limited opportunities for rapid career advancement based solely on performance |
| Structured career path and opportunities for professional development | Salary compression at higher grades |
| Opportunity to serve the nation and make a difference in society | Potential for bureaucracy and slow decision-making processes |
Frequently Asked Questions about "Gred Gaji" and "Elaun"
Here are some common questions about the Malaysian public service salary system:
1. What does "gred gaji" mean?
"Gred gaji" translates to "salary grade" in English. It refers to the hierarchical ranking system used to determine the salary range for a particular position in the Malaysian public service.
2. What are the different salary grades in the Malaysian public service?
The Malaysian public service utilizes a numerical system for salary grades, ranging from the lowest to the highest. For instance, DG41 represents a higher grade (and typically higher salary range) than DG32.
3. How are salary grades determined?
Factors such as academic qualifications, work experience, job complexity, and level of responsibility influence the assigned salary grade for a position.
4. What is "elaun" and what types are there?
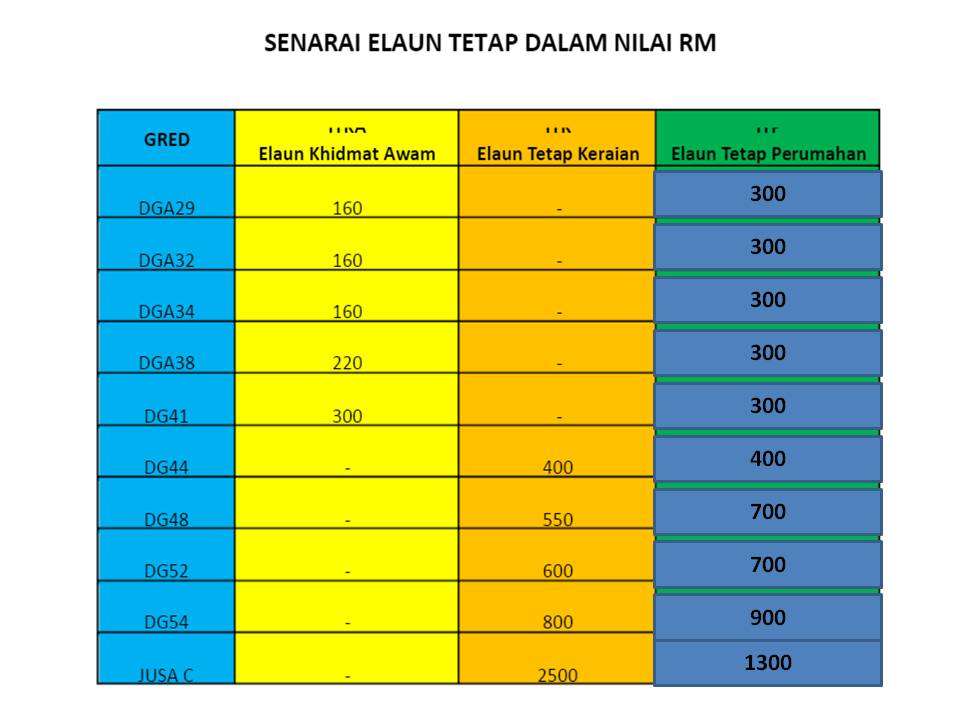
"Elaun" translates to "allowance" in English. These are additional payments on top of the base salary, designed to cover specific expenses or provide incentives for certain roles. Common types include housing allowances, cost of living adjustments, and on-call allowances.
5. How can I learn more about the specific salary grade and allowances for a particular public service position?
Detailed information is usually available on official government websites, including the Public Service Department (JPA) website or specific ministry websites. Job advertisements will often outline the salary grade and key benefits associated with the position.
6. Is there a difference in salary grades and allowances between different government ministries or agencies?
While the general principles of the salary system apply across the public service, there might be slight variations in specific allowances or benefits depending on the ministry, agency, or job requirements.
7. Are salary grades and allowances subject to change?
Yes, the Malaysian government periodically reviews and may adjust salary grades and allowances to keep pace with inflation, cost of living changes, and to ensure the public service remains competitive in attracting and retaining talent.
8. How can I find information about salary increments and promotions within the Malaysian public service?
Policies regarding salary increments and promotions are typically outlined by the Public Service Department (JPA) and are usually based on factors like performance evaluations, years of service, and availability of vacancies in higher grades. Information specific to your ministry or agency will be available through internal communication channels or human resource departments.
Conclusion
The Malaysian public service salary and allowance system is a structured framework designed to provide fair compensation and benefits to civil servants. Understanding the concepts of "gred gaji" and "elaun," and how they contribute to the overall compensation package is crucial for anyone considering or currently pursuing a career in public service. While the public sector offers advantages like job security and a comprehensive benefits package, it's essential to weigh these against potential drawbacks such as slower salary progression compared to the private sector. By being well-informed about the system's intricacies, individuals can make empowered decisions about their career paths and financial well-being within the Malaysian public service.

gred gaji dg48 dan elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai

gred gaji dg48 dan elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai
gred gaji dg48 dan elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai

gred gaji dg48 dan elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai
gred gaji dg48 dan elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai
gred gaji dg48 dan elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai
gred gaji dg48 dan elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai

gred gaji dg48 dan elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai
gred gaji dg48 dan elaun | YonathAn-Avis Hai