Unleash the Beast: Your Guide to 300 Watt Per Channel Amplifiers
Are you ready to experience audio like never before? Imagine sound so pure, so powerful, it sends shivers down your spine. That's the promise of a 300-watt per channel amplifier. But is it all hype, or is there real power behind the promise? This guide dives deep into the world of these audio behemoths, exploring everything from their history and functionality to their practical applications and potential pitfalls.
A 300 watt per channel amplifier represents a significant step up in power output compared to standard receivers or integrated amplifiers. This power translates to an ability to drive even the most demanding speakers with ease, delivering clean, undistorted sound even at high volumes. Think room-filling sound, crisp highs, and deep, resonant bass. Whether you're a dedicated audiophile, a home theater enthusiast, or a musician looking to power a small venue, understanding the nuances of these amplifiers is crucial.
The evolution of audio amplification has been a relentless pursuit of cleaner, more powerful sound reproduction. While the exact origins of the 300-watt per channel amplifier are difficult to pinpoint, they represent a culmination of decades of advancements in amplifier technology. From vacuum tubes to transistors and integrated circuits, each generation has pushed the boundaries of power and fidelity. These higher-power amplifiers became essential as speaker technology evolved, with more complex and power-hungry designs requiring more robust amplification to reach their full potential. This interplay between amplifier and speaker technology continues to drive innovation in the audio world.
One of the key issues related to amplifiers in this power range is heat dissipation. Delivering 300 watts per channel generates significant heat, requiring robust cooling solutions to ensure reliable operation and prevent damage to the amplifier's internal components. This often translates to larger, heavier amplifiers with substantial heat sinks and ventilation systems. Another consideration is power consumption. These amplifiers draw significant current, especially at high output levels. This can impact your electricity bill and may require dedicated power circuits to avoid overloading your home's electrical system.
In simpler terms, a 300 watt per channel amplifier provides 300 watts of power to each individual speaker channel. This means a stereo amplifier with this rating can deliver 300 watts to the left speaker and 300 watts to the right speaker simultaneously. This is crucial for dynamic range, allowing the amplifier to handle sudden peaks in the audio signal without distortion, resulting in a more accurate and impactful listening experience. For example, in a home theater setup, this power ensures that explosions in action movies are rendered with visceral impact, while subtle dialogue remains clear and intelligible.
Three key benefits of a 300 watt per channel amplifier are: 1) Headroom: The amplifier can easily handle dynamic peaks in the music, preventing clipping and distortion. 2) Control: Improved control over the speakers leads to tighter bass response and more accurate sound reproduction. 3) Loudness: While not always the primary goal, these amplifiers can achieve significantly higher volumes without distortion, ideal for larger rooms or outdoor events.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 300 Watt Per Channel Amplifiers
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High power output for demanding speakers | Can be expensive |
| Clean and undistorted sound at high volumes | Requires careful matching with speakers |
| Improved dynamic range and headroom | Generates significant heat |
| Ideal for larger rooms and home theaters | Consumes more power |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Do I need a 300-watt amplifier for my speakers? It depends on the speaker's sensitivity and impedance, as well as the room size.
2. How do I connect my amplifier to my speakers? Use high-quality speaker cables with appropriate connectors.
3. What is impedance matching? Matching the amplifier's output impedance to the speaker's impedance is crucial for optimal performance.
4. Can I use a 300-watt amplifier with lower-powered speakers? Yes, but be cautious with the volume to avoid damaging the speakers.
5. What is clipping? Clipping is a form of distortion that occurs when the amplifier is pushed beyond its limits.
6. How do I prevent overheating? Ensure proper ventilation around the amplifier.
7. What are the different types of 300-watt amplifiers? There are various classes of amplifiers (Class A, Class B, Class AB, Class D) each with different characteristics.
8. What are some recommended brands? Research reputable audio brands known for quality amplifiers.
In conclusion, a 300-watt per channel amplifier offers a compelling combination of power and fidelity, unlocking the full potential of your audio system. While there are considerations regarding heat management and power consumption, the benefits of enhanced dynamic range, improved speaker control, and higher volume capabilities make these amplifiers a worthy investment for serious audio enthusiasts. By carefully considering your specific needs and understanding the technical aspects involved, you can harness the power of a 300-watt amplifier to create a truly immersive and unforgettable listening experience. Take the plunge and elevate your audio experience to a whole new level.

Mono and Stereo High | YonathAn-Avis Hai
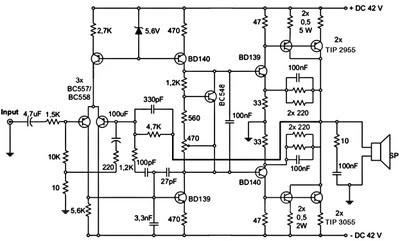
30 Watt Subwoofer Amplifier Circuit Diagram | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Amplifier For 200 Watt Speakers | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Audio Power Amplifier Schematics | YonathAn-Avis Hai

McIntosh MC7300 Stereo Power Amplifier 300 watts per channel x 2 Photo | YonathAn-Avis Hai

McIntosh MC7300 Stereo Power Amplifier 300 watts per channel x 2 Photo | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Toa P300D 300 Watt Per Channel Power Amplifier Photo 883623 | YonathAn-Avis Hai

amplifier 300 watt per channel | YonathAn-Avis Hai

50w Subwoofer Amplifier Circuit Diagram | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Power Amplifier 300 Watt Mono | YonathAn-Avis Hai