Unlocking the GS Employee Salary Puzzle: Your Guide to Step Increases
Imagine a career ladder, not just in terms of promotion, but also in steady, predictable salary growth. For those working within the General Schedule (GS) pay system, this ladder exists in the form of step increases. But how does this system actually work? What are the nuances of the GS employee step increase timeline, and how can you ensure you're making the most of it? This is the deep dive you've been waiting for.
The GS employee step increase timeline is a critical component of the federal government's compensation structure. It provides a clear framework for salary progression within each GS grade, offering employees the potential for regular pay bumps based on time in service and performance. Understanding this system is crucial for anyone navigating a career within the GS framework. It’s not just about the money, though that’s certainly a major motivator. It’s about understanding the system designed to reward dedication and service.
The GS pay scale has a rich history, evolving over decades to become the structured system we see today. Its origins lie in the desire for a standardized, fair, and transparent approach to federal employee compensation. The step increase timeline emerged as a key element of this system, providing a mechanism for recognizing experience and rewarding sustained performance. The system’s importance stems from its ability to attract and retain talent within the government by providing a clear path for financial advancement.
However, the GS employee step increase timeline isn’t without its complexities. One key issue revolves around the waiting periods between steps, which can vary depending on the specific GS grade and step level. Another challenge can be the impact of performance reviews on step progression, highlighting the need for consistent, high-quality work. Navigating these nuances requires a thorough understanding of the regulations and policies governing the GS system.
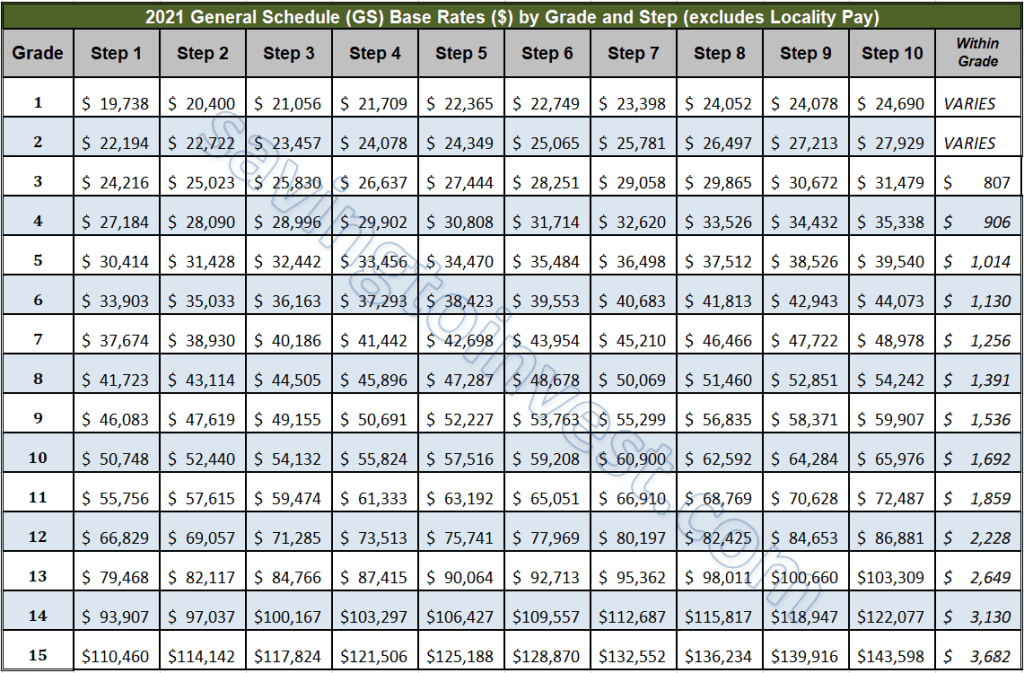
Let's define a few key terms. A "step" represents a specific pay level within a GS grade. Each grade has ten steps, with Step 1 being the entry-level and Step 10 being the highest within that grade. The "step increase timeline" refers to the duration an employee must serve at a particular step before becoming eligible for progression to the next. For example, an employee at GS-7, Step 1 might need to wait one year before advancing to GS-7, Step 2, while the wait between subsequent steps might be two years.
One primary benefit of the GS employee step increase timeline is its predictability. Employees can generally anticipate salary increases based on their time in service. Another advantage is the built-in motivation for career growth. The structured progression encourages employees to strive for excellence and maintain high performance levels. Furthermore, the transparency of the system fosters a sense of fairness and equity in compensation across the federal workforce.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the GS Employee Step Increase Timeline
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Predictable Salary Increases | Potentially Slow Progression at Higher Steps |
| Motivation for Career Growth | Limited Flexibility for Exceptional Performance |
| Transparency and Fairness | Impact of Budget Constraints |
Navigating the GS employee step increase timeline successfully involves understanding the specific regulations for your grade and agency. Stay informed about any changes to the pay scales or policies. Maintain open communication with your supervisor regarding performance expectations and your progress towards step increases.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How often do GS employees get step increases? Generally, step increases occur annually or every two years, depending on the step level.
2. What is a within-grade increase? A within-grade increase is another term for a step increase.
3. Can step increases be withheld? Yes, in certain situations related to performance.
4. What happens at Step 10? Upon reaching Step 10, further salary increases typically require promotion to a higher GS grade.
5. How is the GS pay scale determined? The GS pay scale is set by the Office of Personnel Management (OPM).
6. Does locality pay affect step increases? Locality pay adjustments are separate from step increases but are added to the base salary.
7. Where can I find the latest GS pay tables? The OPM website provides current GS pay tables.
8. What if my performance review is negative? This could potentially impact your step increase.
In conclusion, the GS employee step increase timeline offers a structured path for salary growth within the federal government. While there are potential challenges related to waiting periods and performance requirements, the system's predictability, transparency, and built-in motivation make it a valuable component of the GS compensation structure. Understanding the nuances of the GS step increase timeline empowers employees to plan their careers effectively, maximize their earning potential, and contribute meaningfully to the public sector. By staying informed, engaging with supervisors, and consistently striving for excellence, GS employees can successfully navigate this system and reap the rewards of a stable and rewarding career path.

Federal Government Releases New Salary Table | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Dc Gs Pay Scale 2024 Hourly | YonathAn-Avis Hai
Gs 15 Pay Scale Dc 2023 | YonathAn-Avis Hai

gs employee step increase timeline | YonathAn-Avis Hai

general scale pay 2024 Opm gs pay scale 2024 hourly rate | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Federal employee pay grade scale 2013 | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Gs Pay Scale Table 2024 With Locality | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Federal Pay Raise 2024 Washington Dc | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Gs Pay Scale 2024 With Locality Pay Hawaii | YonathAn-Avis Hai

gs employee step increase timeline | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Gs Pay Scale 2024 Dc Locality Wise List | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Full Time Employee Step Increase Letter | YonathAn-Avis Hai