Unstacking the Code: Understanding Linear Data Structures - Stacks
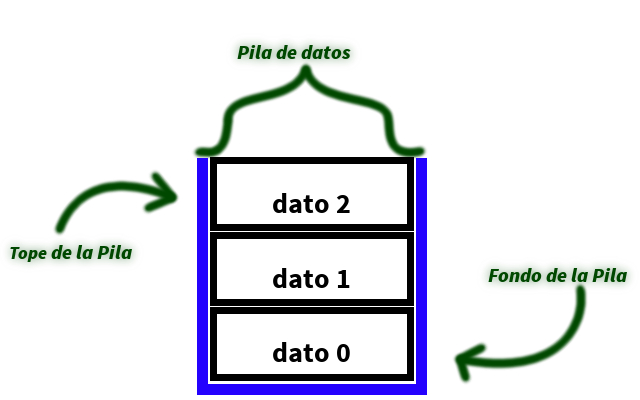
Imagine a stack of plates. You can only add or remove a plate from the top. This simple analogy perfectly illustrates one of the most fundamental concepts in computer science: the stack data structure. In programming, especially when dealing with "estructuras de datos lineales pilas" (linear data structures - stacks), understanding this last-in, first-out (LIFO) principle is key to writing efficient and elegant code.
Stacks are everywhere in programming, even if you don't realize it. From the way your computer manages function calls to the undo button in your text editor, stacks work behind the scenes to ensure everything runs smoothly. This "estructuras de datos lineales pilas" approach might seem limiting at first, but its simplicity is its strength, making it incredibly efficient for a wide range of tasks.
The history of "estructuras de datos lineales pilas" can be traced back to the early days of computer science. One of the earliest mentions of the stack as a data structure came from the work of Alan Turing in the 1940s. Turing, a pioneer in computer science, used the concept of a stack to manage the execution flow of algorithms in his theoretical Turing Machine.
But the importance of "estructuras de datos lineales pilas" goes beyond historical significance. These structures are crucial for tasks like parsing expressions (think calculators and compilers), backtracking algorithms (like those used in maze solving), and memory management in operating systems. Their impact on how we interact with technology is profound, even if it's largely invisible to the average user.
One of the main issues related to "estructuras de datos lineales pilas" is the potential for stack overflow. This occurs when you try to add more elements to a stack than its allocated memory can handle. Imagine our stack of plates again – if you keep piling them on, eventually, the whole thing will come crashing down! That's why understanding the limitations of stacks and using them appropriately is crucial for any programmer.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Stacks
Let's delve into the pros and cons of utilizing stacks in your programming endeavors:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Understanding these trade-offs will guide you in selecting the appropriate data structure for your specific programming challenges. While "estructuras de datos lineales pilas" offer efficiency and clarity in certain scenarios, they are not a one-size-fits-all solution.
As you venture further into the world of programming, familiarizing yourself with various data structures like "estructuras de datos lineales pilas" (linear data structures - stacks) will significantly enhance your ability to design elegant, efficient, and robust solutions.

Las estructuras de datos es una rama de las ciencias de la computación | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Estructuras de Datos Lineales / 978 | YonathAn-Avis Hai

estructuras de datos lineales pilas | YonathAn-Avis Hai
estructuras de datos lineales pilas | YonathAn-Avis Hai

¿Qué es una estructura de datos en programación? | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Pilas, colas, y listas estructura de datos | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Estructuras de datos: diferencias entre PILAS y COLAS | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Universidad Autónoma del Estado de México | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Departamento de Ingeniería de Sistemas e Industrial | YonathAn-Avis Hai
Clasificación de las estructuras de datos, Hecho por: Luis Alberto | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Estructuras de datos jerárquicas | YonathAn-Avis Hai

estructuras de datos lineales pilas | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Pilas y Colas: Estructuras de Datos Lineales para Insertar y | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Estructura Lineal Estructura De Datos Youtube | YonathAn-Avis Hai

Torpe En lo que respecta a las personas Inicialmente pilas estructura | YonathAn-Avis Hai